Understand SSO
Single Sign-On (SSO) is an authentication method that allows users to access multiple applications and websites with a single set of login credentials, eliminating the need for users to remember and manage separate usernames and passwords for each application and providing a more streamlined and secure login experience.
To manage SSO, you must have the Admin role.
How SSO Works
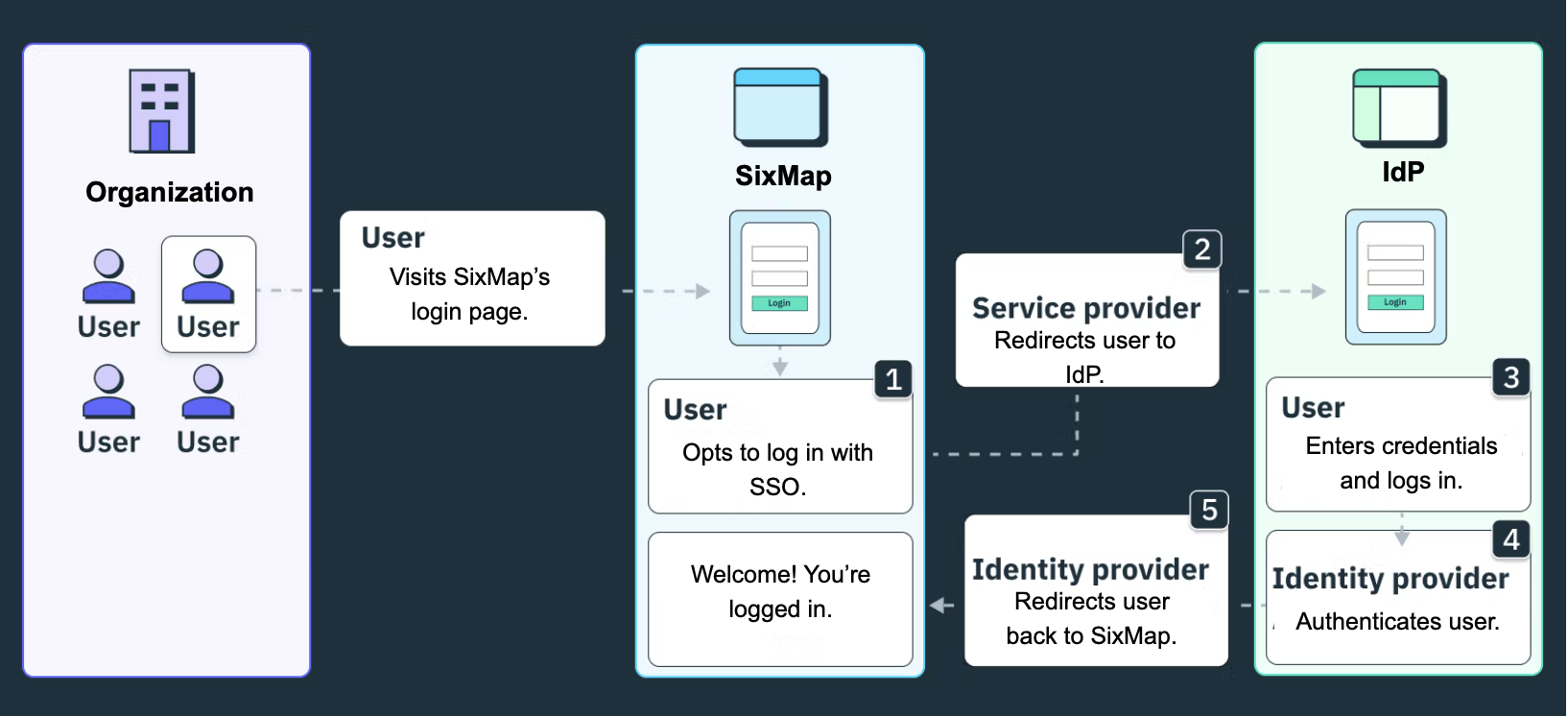
- A user navigates to the SixMap login page and selects Continue with SSO.
- SixMap redirects the user to their organization's Identity Provider (IdP). The IdP service, such as Okta or Google Workspace, manages user identities and authentication.
- The user authenticates with the IdP using their existing organizational credentials, such as username and password.
- After the user successfully authenticates, the IdP generates a security assertion or token. This token contains information about the user's identity and, in some cases, their authorization level.
- The IdP sends the security assertion or token back to SixMap, and SixMap uses the information, including any attribute statements, to verify the user and grant access to the app.
Attribute statements
Attribute statements are key-value pairs that provide specific information about a user. IdPs include them in the security assertion or token sent during step four of the SSO process. The "key" is a label for the information (e.g., email, firstName), and the "value" is the specific data for that user (e.g., [email protected], John).
-
Common attributes such as
email,firstName,lastName, allow SixMap to match the authenticated user to their corresponding account. For information about how to map your organization's attributes, see Edit SSO connection details. -
If your organization integrates with your SSO identity provider (IdP) through SCIM, admins can use the as
groupsattribute from your IdP to map to SixMap roles. For more information, see SCIM.
SSO Protocols
SSO relies on Identity Providers (IdPs) to manage user authentication. An Identity Provider (IdP) is a service that stores and manages digital identities. It authenticates users and provides authorization to access resources, such as applications like SixMap. Popular IdPs include Okta, Google Workspace, and Microsoft Entra ID.
These IdPs typically support common SSO protocols, which are standards that define how IdPs and applications exchange authentication and authorization information. Two of the most prevalent protocols are:
- SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language): A mature, XML-based open standard used for exchanging authentication and authorization data between identity providers (IdPs) and service providers (SPs), such as SixMap. Enterprise organizations often use SAML, particularly with web-based applications where security and detailed authorization are necessary.
- OIDC (OpenID Connect): An identity layer built on the OAuth 2.0 authorization framework. OIDC is a modern, RESTful protocol that enables identity verification and single sign-on for web and mobile applications.
SixMap offers flexibility in how it connects to your IdP. SixMap supports common IdPs, such as Okta, Google Workspace, and Microsoft Entra ID. SixMap also supports custom SAML and OIDC connections.
To configure a custom connection, you'll need the Source Organization ID and Source Connection ID.
- Source Organization ID: This is a unique identifier for your organization within your IdP's system. It's how your IdP distinguishes your organization from others. You can typically find this ID in your IdP's administration console or developer settings.
- Source Connection ID: This is a unique identifier for your organization's specific SSO connection configured within your IdP. If you have multiple SSO connections, each will have a different Connection ID. This ID is typically available in your IdP's administration console or developer settings.